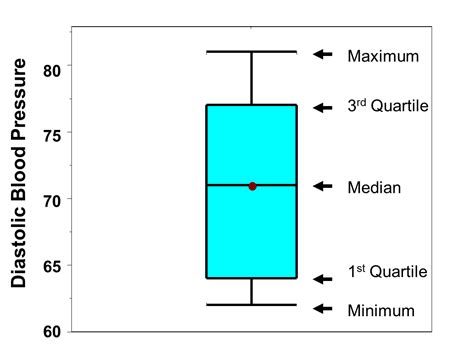
shape of distribution using a box plot Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
$225.00
0 · symmetric box and whisker plot
1 · skewness on a box plot
2 · skewed box and whisker plot
3 · shape of distribution skewed right
4 · shape of distribution skewed left
5 · right skewed data box plot
6 · right skewed box plot vertical
7 · explain box plot with example
$39.00
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format. Analysts frequently use them during exploratory . See moreInstead of displaying the raw data points, a box and whisker plot takes your sample data and presents ranges of values based on quartiles using . See more
A box and whisker plot allows you quickly assess a distribution’s central tendency, variability, and skewness. Let me show you how! See more
Let’s combine all we’ve learned about box plots and compare four groups in this example. Suppose we have four groups of test scores and we want to compare them by teaching method. . See more Box plots are useful as they show the skewness of a data set. The box plot shape will show if a statistical data set is normally distributed or skewed. When the median is in the middle of the box, and the whiskers are about the .Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], . A box plot chart visualizes the distribution of a dataset using five key statistics: minimum, Q1, median, Q3, and maximum. It’s an efficient way to identify outliers and .
A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with . This graph summarizes basic statistics for calories and displays the distribution of the data, highlighting that the data are skewed and that the data are not from a normal distribution. Box plots highlight outliers. Box plots help you . Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median .Question: 1. Describe the shape of the distribution of the Year_1 variable using statistical terminology. 2. If you were presenting these data (e.g., conference presentation, presentation to coworkers), would you use the histogram or .
symmetric box and whisker plot
About; Statistics; Number Theory; Java; Data Structures; Cornerstones; Calculus; Shape, Center, and Spread of a Distribution. A population parameter is a characteristic or measure obtained by using all of the data values in a population.. A sample statistic is a characteristic or measure obtained by using data values from a sample.. The parameters and statistics with which we .
skewness on a box plot
Distribution Shape; Central Value of it; Variability of it; A box plot is a chart that shows data from a five-number summary including one of the measures of central tendency. It does not show the distribution in particular as much as a stem .Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right. The term “box plot” refers to an outlier box plot; this plot is also called a box-and-whisker plot or a Tukey box plot. See the "Comparing outlier and quantile box plots" section below for another type of box plot. Here are the basic parts of a box plot: The center line in the box shows the median for the data. Half of the data is above .a distribution that can be divided at the center so each half is the mirror of the other. Box Plot. A diagram of range, median, and interquartile range. Median. A measure of center found by determining the middle number in a data set arranged in numerical order. Lower Quartile (Q1)
The box plot shows the undergraduate in-state tuition per credit hour at four-year public colleges. 0 150 300 450 600 750 900 1050 1200 1350 1500 a. Estimate the median. . What do you conclude about the shape of the distribution of component size? Mild positive skewness Mild negative skewness c Determine the first and third quartiles. Do not .
Describe the shape of a dot plotIn this lesson you will learn about the shape of the distribution of data by looking at various graphs and observing symmetry. By using Box plot you can provide a summary of the distribution, identify potential and compare different datasets in a compact and visual manner. . Information that are missed in a box plot is the detailed shape of the distribution. It is quite difficult to find the mean as it is visual representation of the data.
1. Arrange data in ascending order 2. Find the median, Q1, Q3. 4. Calculate IQR (Q3-Q1) 5. Multiply IQR by 1.5 - Subtract 1.5IQR from Q1 to determine outliers - Add 1.5IQR to Q3 to determine outliers 6. Identify 5 number summary (find new max/min if necessary) 7. Add outliers beyond the fences w/ * or special symbols 8. Draw boxplot!
The term “box plot” refers to an outlier box plot; this plot is also called a box-and-whisker plot or a Tukey box plot. See the "Comparing outlier and quantile box plots" section below for another type of box plot. Here are the basic parts of a box plot: The center line in the box shows the median for the data. Half of the data is above .The 'Shape of Distribution' refers to the pattern or form taken by data points when plotted on a graph, indicating how values are spread out across different categories or ranges. . The box plot shows the median, upper and lower quartiles, outliers, and minimum and maximum values. A stem and leaf plot is similar to a histogram but shows more . The term “box plot” refers to an outlier box plot; this plot is also called a box-and-whisker plot or a Tukey box plot. See the "Comparing outlier and quantile box plots" section below for another type of box plot. Here are the basic parts of a box plot: The center line in the box shows the median for the data. Half of the data is above .
The term “box plot” refers to an outlier box plot; this plot is also called a box-and-whisker plot or a Tukey box plot. See the "Comparing outlier and quantile box plots" section below for another type of box plot. Here are the basic parts of a box plot: The center line in the box shows the median for the data. Half of the data is above . A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], .
electrical box certificate
VIDEO ANSWER: this question, just ask us to explain how to tell the shape of a box plot. Um Using the whiskers and the median. So I've drawn an example of three different shapes just so that it will help us think a . Um So if .
electrical box covering
Find step-by-step Statistics solutions and the answer to the textbook question Use the given box-and-whisker plot to determine if the shape of the distribution represented is symmetric, skewed left, skewed right, or none of these. Justify your answer.. Summary: A Box Plot is a graphical representation summarising data distribution through key statistics like quartiles and outliers.It visualises central tendencies and variability, making it invaluable for Data Analysis. Introduction. Data Visualisation is crucial in transforming complex datasets into clear, visual formats, allowing for quick insights and decision-making.
The median value has nothing to do with the shape of the distribution. In fact, that's the point I was making by showing the histogram and the boxplot together. The median value doesn't indicate the expected value of a skewed distribution which is why the boxplot isn't the best representation of a skewed distribution. For a scalar random variable, the following plots are all useful depictions of the distribution: The box plot: This is a simple plot that shows various quantiles of the data using a standard box-and-whiskers method, as well as showing "outliers" that are outside some multiple of the interquartile range. This plot gives a simple sense of where the bulk of the data lies, via .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A dot plot is best applied when____ A) A single variable is summarised B) The mean, median, and mode are equal C) The general shape of distribution is symmetric D) The relationship between two variables is summarised, A dot plot can be used to show ___ A) The mean, median, and mode B) The . Box plots, also called box and whisker plots, are more useful than histograms for comparing distributions. . The shape of this distribution is described better with more intervals than we had .Assessing the symmetry of a distribution using a box plot is straightforward. Symmetry means that the data is evenly distributed on both sides of the center. To check for symmetry, observe the box plot: If the box and whiskers are approximately equal in length on both sides of the median (Q2), the data distribution is symmetric.The distribution shape can give you a visual which helps to show how the data is: Spread out (e.g. dispersion, variability, scatter), Where the mean lies, What the range of the data set is, . A symmetric box plot has the “box” in the center of the graph: A symmetric box plot. 3. Skewness.
A box plot summarizes the data and indicates the median, upper and lower quartiles, and minimum and maximum values. . the whisker cap shape, and the visual attributes for the mean marker, median line, and the connect lines. . The most common density plot uses the normal distribution, which is defined by the mean and the standard deviation. . Combining violin plots and box plots can offer a detailed view of the data distribution, making it easier to spot the overall shape (via the violin plot) while also observing key summary statistics like the median, quartiles, and outliers (via the box plot). However, aligning them side by side, especially with dodging (i.e., separating the plots fo
The term “box plot” refers to an outlier box plot; this plot is also called a box-and-whisker plot or a Tukey box plot. See the "Comparing outlier and quantile box plots" section below for another type of box plot. Here are the basic parts of a box plot: The center line in the box shows the median for the data. Half of the data is above .
skewed box and whisker plot
I'd cut the old siding more or less flush to the box, extending the cuts straight down to the bottom, leaving the old siding behind everything. Then use 1x4's, cut to proper width, to frame in the old siding and creating a clean edge for your foam and new siding to butt against.
shape of distribution using a box plot|symmetric box and whisker plot